A patient undergoing immunosuppressive therapy will develop serum sickness, a symptom resulting from the presence of excess antibodies in the blood. This syndrome can be caused by a viral illness or an infection that occurs as a result of an autoimmune disorder. It can occur at any stage of life but is most common during the early stages of immunotherapy treatment.
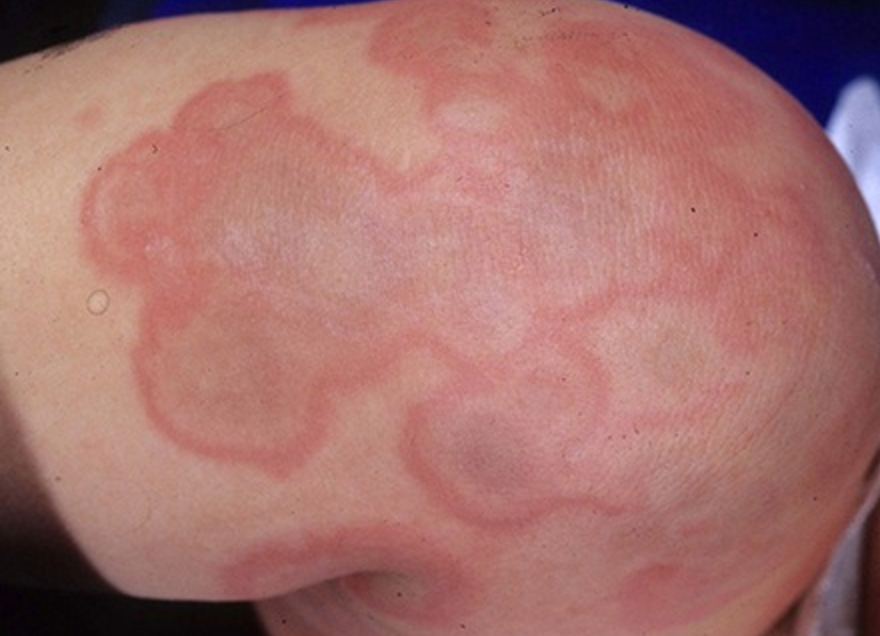
When antibodies are present, the immune system’s ability to fight infection is reduced and can cause a secondary infection of the body. Some patients who are infected with measles can also develop this syndrome.
The body produces antibodies as a defense against infections, but there is an increased risk of developing antibodies when your immune system is weakened due to an auto-immune disease like HIV or AIDS. A patient who is immunosuppressed will develop serum sickness if he has been infected with a virus that stimulates the production of antibodies.
What is serum sickness? A person infected with measles will normally have symptoms such as fever, swollen glands, headache, vomiting and diarrhea, but some can experience a more severe and disabling disease known as measles encephalitis. In this disease, fluid filled in the brain is present. Severe outbreaks can be deadly and even cause death.
Symptoms include weakness, dizziness, irritability, vomiting, and diarrhea. The elderly and those with poor immunity can also develop serum sickness.
The treatment protocol for the illness varies from patient to patient. It depends on the stage of disease, the type of virus and the extent of antibodies present in the bloodstream. For milder cases, doctors generally use drugs that decrease the production of antibodies. This is done with either intravenous medications or systemic drugs. These include azathioprine or pentamycin.
This treatment protocol is also used for children and adults who have immune system disorders such as HIV/AIDS, measles, and measles encephalitis. These patients can also benefit from the administration of immunoglobulin, which enhances the body’s immune response to fight against infectious agents.
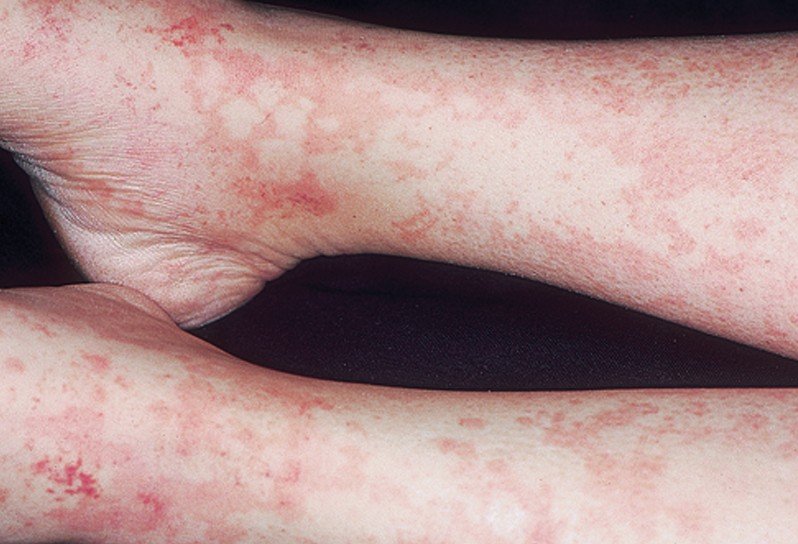
There is no cure for serum sickness. The only way to prevent its onset is through vaccination, usually at birth. In severe cases, patients are given immunosuppressive drugs to suppress the antibodies and undergo treatment. Other ways to treat it include oral or intravenous immunoglobulin and intravenous vaccines.
In a severe case, doctors may perform surgery. It is necessary to get immediate medical attention if you see symptoms of infection, including fever, headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, etc. Do not hesitate to seek immediate help as there could be serious problems developing.
Symptoms of pneumonia can also occur. This is when the lungs and other parts of the body become congested with fluid.
Cases of hepatitis and influenza can also cause fever and chills. If not treated, these diseases can lead to serious complications.
Serum sickness is also commonly accompanied by jaundice, which is the most common symptoms. The symptoms of jaundice include a yellow or greenish skin rash that occurs on the face, neck, scalp and upper chest.
There are other rarer but more serious conditions that can result from serum sickness. These include hepatitis B, HIV, tuberculosis and typhoid.
The most common types of treatments include immunodeficiency therapy (IVT), in which patients receive medications that enhance the body’s immune response to fight against infectious agents. This can help to reduce the chances of developing these diseases. Antibiotics are also used to treat serum sickness in order to prevent the development of infections.
However, some side effects of the medications can cause side effects of their own. So it is important to be aware of any potential risks before deciding to use them.
Side effects can range from mild to severe. Some patients develop symptoms of jaundice and liver damage. Others experience skin irritation and abdominal cramps.
Treatment protocol varies depending on the type of disease. The treatment process can take anywhere from a few days to several months.